Adjusted Basis
While you own your home, various events may take place that can change the original basis of your home. These events can increase or decrease your original basis. The result is called adjusted basis. See Table 3, earlier, for a list of some of the items that can adjust your basis.
Improvements. An improvement materially adds to the value of your home, considerably prolongs its useful life, or adapts it to new uses. You must add the cost of any improvements to the basis of your home. You cannot deduct these costs.
Improvements include putting a recreation room in your unfinished basement, adding another bathroom or bedroom, putting up a fence, putting in new plumbing or wiring, installing a new roof, and paving your driveway.
Amount added to basis. The amount you add to your basis for improvements is your actual cost. This includes all costs for material and labor, except your own labor, and all expenses related to the improvement. For example, if you had your lot surveyed to put up a fence, the cost of the survey is a part of the cost of the fence.
You also must add to your basis state and local assessments for improvements such as streets and sidewalks if they increase the value of the property. These assessments are discussed earlier under Real Estate Taxes.
Repairs versus improvements. A repair keeps your home in an ordinary, efficient operating condition. It does not add to the value of your home or prolong its life. Repairs include repainting your home inside or outside, fixing your gutters or floors, fixing leaks or plastering, and replacing broken window panes. You cannot deduct repair costs and generally cannot add them to the basis of your home.
However, repairs that are done as part of an extensive remodeling or restoration of your home are considered improvements. You add them to the basis of your home.
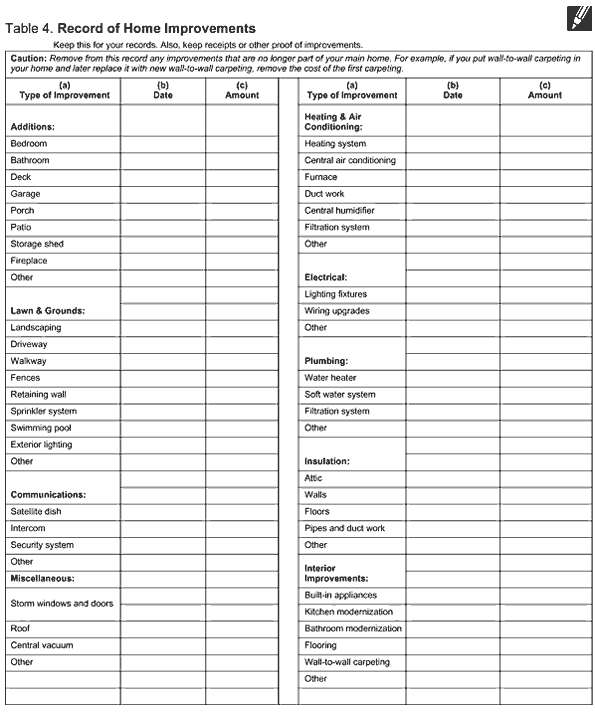
Records to keep. You can use Table 4 (at the end of the publication) as a guide to help you keep track of improvements to your home. Also see Keeping Records, later.
Energy conservation subsidy. If a public utility gives you (directly or indirectly) a subsidy for the purchase or installation of an energy conservation measure for your home, do not include the value of that subsidy in your income. You must reduce the basis of your home by that value.
An energy conservation measure is an installation or modification primarily designed to reduce consumption of electricity or natural gas or to improve the management of energy demand.
Keeping Records
 Keeping full and accurate records is vital to properly report your income and expenses, to support your deductions and credits, and to know the basis or adjusted basis of your home. These records include your purchase contract and settlement papers if you bought the property, or other objective evidence if you acquired it by gift, inheritance, or similar means. You should keep any receipts, canceled checks, and similar evidence for improvements or other additions to the basis. In addition, you should keep track of any decreases to the basis such as those listed in Table 3.
Keeping full and accurate records is vital to properly report your income and expenses, to support your deductions and credits, and to know the basis or adjusted basis of your home. These records include your purchase contract and settlement papers if you bought the property, or other objective evidence if you acquired it by gift, inheritance, or similar means. You should keep any receipts, canceled checks, and similar evidence for improvements or other additions to the basis. In addition, you should keep track of any decreases to the basis such as those listed in Table 3.
How to keep records. How you keep records is up to you, but they must be clear and accurate and must be available to the IRS.
How long to keep records. You must keep your records for as long as they are important for meeting any provision of the federal tax law.
Keep records that support an item of income, a deduction, or a credit, appearing on a return until the period of limitations for the return runs out. (A period of limitations is the period of time after which no legal action can be brought.) For assessment of tax you owe, this is generally 3 years from the date you filed the return. For filing a claim for credit or refund, this is generally 3 years from the date you filed the original return, or 2 years from the date you paid the tax, whichever is later. Returns filed before the due date are treated as filed on the due date.
You may need to keep records relating to the basis of property (discussed earlier) longer than for the period of limitations. Keep those records as long as they are important in figuring the basis of the original or replacement property. Generally, this means for as long as you own the property and, after you dispose of it, for the period of limitations that applies to you.
How To Get Tax Help
You can get help with unresolved tax issues, order free publications and forms, ask tax questions, and get more information from the IRS in several ways. By selecting the method that is best for you, you will have quick and easy access to tax help.
Contacting your Taxpayer Advocate. If you have attempted to deal with an IRS problem unsuccessfully, you should contact your Taxpayer Advocate.
The Taxpayer Advocate represents your interests and concerns within the IRS by protecting your rights and resolving problems that have not been fixed through normal channels. While Taxpayer Advocates cannot change the tax law or make a technical tax decision, they can clear up problems that resulted from previous contacts and ensure that your case is given a complete and impartial review.
To contact your Taxpayer Advocate:
- Call the Taxpayer Advocate at
1-877-777-4778.
- Call, write, or fax the Taxpayer Advocate office in your area.
- Call 1-800-829-4059 if you are a
TTY/TDD user.
For more information, see Publication 1546, The Taxpayer Advocate Service of the IRS.
Free tax services. To find out what services are available, get Publication 910, Guide to Free Tax Services. It contains a list of free tax publications and an index of tax topics. It also describes other free tax information services, including tax education and assistance programs and a list of TeleTax topics.
 Personal computer. With your personal computer and modem, you can access the IRS on the Internet at www.irs.gov. While visiting our web site, you can:
Personal computer. With your personal computer and modem, you can access the IRS on the Internet at www.irs.gov. While visiting our web site, you can:
- See answers to frequently asked tax questions or request help by e-mail.
- Download forms and publications or search for forms and publications by topic or keyword.
- Order IRS products on-line.
- View forms that may be filled in electronically, print the completed form, and then save the form for recordkeeping.
- View Internal Revenue Bulletins published in the last few years.
- Search regulations and the Internal Revenue Code.
- Receive our electronic newsletters on hot tax issues and news.
- Learn about the benefits of filing electronically (IRS e-file).
- Get information on starting and operating a small business.
You can also reach us with your computer using File Transfer Protocol at ftp.irs.gov.
 TaxFax Service. Using the phone attached to your fax machine, you can receive forms and instructions by calling 703-368-9694. Follow the directions from the prompts. When you order forms, enter the catalog number for the form you need. The items you request will be faxed to you.
TaxFax Service. Using the phone attached to your fax machine, you can receive forms and instructions by calling 703-368-9694. Follow the directions from the prompts. When you order forms, enter the catalog number for the form you need. The items you request will be faxed to you.
For help with transmission problems, call the FedWorld Help Desk at 703-487-4608.
 Phone. Many services are available by phone.
Phone. Many services are available by phone.
- Ordering forms, instructions, and publications. Call 1-800-829-3676 to order current and prior year forms, instructions, and publications.
- Asking tax questions. Call the IRS with your tax questions at 1-800-829-1040.
- Solving problems.Take advantage of Everyday Tax Solutions service by calling your local IRS office to set up an in-person appointment at your convenience. Check your local directory assistance or www.irs.govfor the numbers
- TTY/TDD equipment. If you have access to TTY/TDD equipment, call 1-800-829- 4059 to ask tax questions or to order forms and publications.
- TeleTax topics. Call 1-800-829-4477 to listen to pre-recorded messages covering various tax topics.
Evaluating the quality of our telephone services. To ensure that IRS representatives give accurate, courteous, and professional answers, we use several methods to evaluate the quality of our telephone services. One method is for a second IRS representative to sometimes listen in on or record telephone calls. Another is to ask some callers to complete a short survey at the end of the call.
 Walk-in.
Walk-in.
- Products. You can walk in to many post offices, libraries, and IRS offices to pick up certain forms, instructions, and publications. Some IRS offices, libraries, grocery stores, copy centers, city and county governments, credit unions, and office supply stores have an extensive collection of products available to print from a CD-ROM or photocopy from reproducible proofs. Also, some IRS offices and libraries have the Internal Revenue Code, regulations, Internal Revenue Bulletins, and Cumulative Bulletins available for research purposes.
- Services. You can walk in to your local IRS office to ask tax questions or get help with a tax problem. Now you can set up an appointment by calling the local IRS office number and, at the prompt, leaving a message requesting Everyday Tax Solutions help. A representative will call you back within 2 business days to schedule an in-person appointment at your convenience.
 Mail. You can send your order for forms, instructions, and publications to the Distribution Center nearest to you and receive a response within 10 workdays after your request is received. Find the address that applies to your part of the country.
Mail. You can send your order for forms, instructions, and publications to the Distribution Center nearest to you and receive a response within 10 workdays after your request is received. Find the address that applies to your part of the country.
- Western part of U.S. :
Western Area Distribution Center
Rancho Cordova, CA 95743-0001
- Central part of U.S.:
Central Area Distribution Center
P.O. Box 8903
Bloomington, IL 61702-8903
- Eastern part of U.S. and foreign addresses:
Eastern Area Distribution Center
P.O. Box 85074
Richmond, VA 23261-5074
 CD-ROM for tax products.You can order IRS Publication 1796, Federal Tax Products on CD-ROM, and obtain:
CD-ROM for tax products.You can order IRS Publication 1796, Federal Tax Products on CD-ROM, and obtain:
- Current tax forms, instructions, and publications.
- Prior-year tax forms and instructions.
- Popular tax forms that may be filled in electronically, printed out for submission, and saved for recordkeeping.
- Internal Revenue Bulletins.
The CD-ROM can be purchased from National Technical Information Service (NTIS) by calling 1-877-233-6767 or on the Internet at www.irs.gov/cdorders. The first release is available in early January and the final release is available in late February.
 CD-ROM for small businesses. IRS Publication 3207, Small Business Resource Guide, is a must for every small business owner or any taxpayer about to start a business. This handy, interactive CD contains all the business tax forms, instructions and publications needed to successfully manage a business. In addition, the CD provides an abundance of other helpful information, such as how to prepare a business plan, finding financing for your business, and much more. The design of the CD makes finding information easy and quick and incorporates file formats and browsers that can be run on virtually any desktop or laptop computer.
CD-ROM for small businesses. IRS Publication 3207, Small Business Resource Guide, is a must for every small business owner or any taxpayer about to start a business. This handy, interactive CD contains all the business tax forms, instructions and publications needed to successfully manage a business. In addition, the CD provides an abundance of other helpful information, such as how to prepare a business plan, finding financing for your business, and much more. The design of the CD makes finding information easy and quick and incorporates file formats and browsers that can be run on virtually any desktop or laptop computer.
It is available in March. You can get a free copy by calling 1-800-829-3676 or by visiting the website at www.irs.gov/smallbiz.
Previous | First
Publication Index | 2002 Tax Help Archives | Tax Help Archives | Home
