Line Instructions for Form 1040NR-EZ
Identifying Number and Address
Identifying Number. You are generally required to enter your social security number (SSN). To apply for an SSN, get Form SS-5 from a Social Security Administration (SSA) office or, if in the United States, you may call the SSA at 1-800-772-1213. Fill in Form SS-5 and return it to the SSA.
If you do not have an SSN and are not eligible to get one, you must get an individual taxpayer identification number (ITIN). To apply for an ITIN, file Form W-7 with the IRS. It usually takes about 4-6 weeks to get an ITIN. Enter your ITIN wherever your SSN is requested on your tax return.
Note: An ITIN is for tax use only. It does not entitle you to social security benefits or change your employment or immigration status under U.S. law.
An incorrect or missing identifying number may increase your tax or reduce your refund.
P.O. Box. Enter your box number only if your post office does not deliver mail to your home.
Foreign Address. Enter the information in the following order: City, province or state, and country. Follow the country's practice for entering the postal code. Do not abbreviate the country name.
Filing Status
Lines 1 and 2. The amount of your tax depends on your filing status. Before you decide which box to check, read the following explanations.
Were You Single or Married? If you were married on December 31, consider yourself married for the whole year. If you were single, divorced, or legally separated under a decree of divorce or separate maintenance on December 31, consider yourself single for the whole year. If you meet the tests described under Married persons who live apart below, you may consider yourself single for the whole year.
If your spouse died in 2002, consider yourself married to that spouse for the whole year, unless you remarried before the end of 2002.
Married persons who live apart. Some married persons who have a child and who do not live with their spouse may file as single. If you meet all five of the following tests and you are a married resident of Canada, Mexico, Japan, or the Republic of Korea (South Korea), or you are a married U.S. national, check the box on line 1.
- You file a return separate from your spouse.
- You paid more than half of the cost to keep up your home in 2002.
- You lived apart from your spouse during the last six months of 2002.
- Your home was the principal home of your child, stepchild, or adopted child for more than half of 2002 or was the principal home of your foster child for all of 2002.
- You are eligible to claim a dependency exemption for the child (on Form 1040NR). However, you can still meet the test if the child's other parent claims him or her as a dependent under the rules in Pub. 501 for children of divorced or separated parents.
Rounding Off to Whole Dollars
To round off cents to the nearest whole dollar on your forms and schedules, drop amounts under 50 cents and increase amounts from 50 to 99 cents to the next dollar. If you do round off, do so for all amounts. But if you have to add two or more amounts to figure the amount to enter on a line, include cents when adding and only round off the total.
Taxable Income
Line 3 - Wages, Salaries, Tips, etc. Enter the total of your effectively connected wages, salaries, tips, etc. For most people, the amount to enter on this line should be shown in box 1 of their Form(s) W-2. However, do not include on line 3 amounts exempted under a tax treaty. Instead, include these amounts on line 6 and complete item J on page 2 of Form 1040NR-EZ. Also include on line 3:
- Wages received as a household employee for which you did not receive a W-2 form because your employer paid you less than $1,300 in 2002. Also, enter HSH and the amount not reported on a W-2 form on the dotted line next to line 3.
- Tip income you did not report to your employer. Also include allocated tips shown on your W-2 form(s) unless you can prove that you received less. Allocated tips should be shown in box 8 of your W-2 form(s). They are not included as income in box 1. See Pub. 531 for more details.
 You may owe social security and Medicare tax on unreported or allocated tips. See the instructions for line 16 on page 6.
You may owe social security and Medicare tax on unreported or allocated tips. See the instructions for line 16 on page 6.
Disability pensions shown on Form 1099-R if you have not reached the minimum retirement age set by your employer.
Note: You must use Form 1040NR to report disability pensions received after you reach your employer's minimum retirement age and other payments shown on Form 1099-R.
Missing or Incorrect Form W-2. Your employer is required to provide or send Form W-2 to you no later than January 31, 2003. If you do not receive it by early February, ask your employer for it. Even if you do not get a Form W-2, you must still report your earnings on line 3. If you lose your Form W-2 or it is incorrect, ask your employer for a new one.
Dependent Care Benefits. If you received benefits for 2002 under your employer's dependent care plan, you must use Form 1040NR. The benefits should be shown in box 10 of your W-2 form(s).
Adoption Benefits. If you received employer-provided adoption benefits for 2002, you must use Form 1040NR. The benefits should be shown in box 12 of your W-2 form(s) with code T.
Tax-Exempt Interest. Certain types of interest income from investments in state and municipal bonds and similar instruments are not taxed by the United States. If you received such tax-exempt interest income, enter TEI and the amount of your tax-exempt interest on the dotted line next to line 3. Include any exempt-interest dividends from a mutual fund or other regulated investment company. But do not include interest earned on your IRA or Coverdell education savings account, or interest from a U.S. bank, savings and loan association, credit union, or similar institution (or from certain deposits with U.S. insurance companies) that is exempt from tax under a tax treaty or under section 871(i) because the interest is not effectively connected with a U.S. trade or business. Do not add any tax-exempt interest into your line 3 total.
Line 4 - Taxable Refunds, Credits, or Offsets of State and Local Income Taxes. If you received a refund, credit, or offset of state or local income taxes in 2002, you may receive a Form 1099-G. If you chose to apply part or all of the refund to your 2002 estimated state or local income tax, the amount applied is treated as received in 2002.
For details on how to figure the amount you must report as income, see Recoveries in Pub. 525.
Line 5 - Scholarship and Fellowship Grants. If you received a scholarship or fellowship, part or all of it may be taxable.
If you were a degree candidate, the amounts you used for expenses other than tuition and course-related expenses (fees, books, supplies, and equipment) are generally taxable. For example, amounts used for room, board, and travel are generally taxable.
If you were not a degree candidate, the full amount of the scholarship or fellowship is generally taxable. Also, amounts received in the form of a scholarship or fellowship that are payment for teaching, research, or other services are generally taxable as wages even if the services were required to get the grant.
If the grant was reported on Form(s) 1042-S, you must generally include the amount shown in box 2 of Form(s) 1042-S on line 5. However, if any or all of that amount is exempt by treaty, do not include the treaty-exempt amount on line 5. Instead, include the treaty-exempt amount on line 6 and complete item J on page 2 of Form 1040NR-EZ.
Attach any Form(s) 1042-S you received from the college or institution. If you did not receive a Form 1042-S, attach a statement from the college or institution (on their letterhead) showing the details of the grant.
For more information about scholarships and fellowships in general, see Pub. 520.
Example 1. You are a citizen of a country that has not negotiated a tax treaty with the United States. You are a candidate for a degree at ABC University (located in the United States). You are receiving a full scholarship from ABC University. The total amounts you received from ABC University during 2002 are as follows:
| Tuition and fees
|
$25,000
|
| Books, supplies, and equipment
|
1,000
|
| Room and board
|
9,000
|
|
|
$35,000
|
Note: Box 2 shows only $9,000 because withholding agents (such as ABC University) are not required to report section 117 amounts (tuition, fees, books, supplies, and equipment) on Form 1042-S.
When completing Form 1040NR-EZ:
- Enter on line 5 the $9,000 shown in box 2 of Form 1042-S.
- Enter $0 on line 9. Because section 117 amounts (tuition, fees, books, supplies, and equipment) were not included in box 2 of your Form 1042-S (and are not included on line 5 of Form 1040NR-EZ), you cannot exclude any of the section 117 amounts on line 9.
- Include on line 18 the $1,260 shown in box 7 of Form 1042-S.
Example 2. The facts are the same as in Example 1 except that you are a citizen of a country that has negotiated a tax treaty with the United States and you were a resident of that country immediately before leaving for the United States to attend ABC University. Also, assume that, under the terms of the tax treaty, all of your scholarship income is exempt from tax because ABC University is a nonprofit educational organization.
Note: Many tax treaties do not permit an exemption from tax on scholarship or fellowship grant income unless the income is from sources outside the United States. If you are a resident of a treaty country, you must know the terms of the tax treaty between the United States and the treaty country to claim treaty benefits on Form 1040NR-EZ. See the instructions for item J on page 8 for details.
When completing Form 1040NR-EZ:
- Be sure you have entered your home country and permanent residence address in the space provided on page 1.
- Enter $0 on line 5. The $9,000 reported to you in box 2 of Form 1042-S is reported on line 6 (not line 5).
- Enter $9,000 on line 6.
- Enter $0 on line 9. Because none of the $9,000 reported to you in box 2 of Form 1042-S is included in your income, you cannot exclude it on line 9.
- Include on line 18 any withholding shown in box 7 of Form 1042-S.
- Provide all the required information in item J on page 2.
Line 6. Use line 6 to report your total effectively connected income that is exempt from tax by a tax treaty. Do not include this exempt income on line 7. Also, you must complete item J on page 2 of Form 1040NR-EZ.
Student Loan Interest Deduction Worksheet - Line 8 (keep for your records)
Before you begin:
- Complete Form 1040NR-EZ, line 9, if it applies to you.
- See the instructions for line 8 above.
|
| 1.
|
Enter the total interest you paid in 2002 on qualified student loans (defined above). Do not enter more than $2,500
|
1.
|
|
| 2.
|
Enter the amount from Form 1040NR-EZ, line 7
|
2.
|
|
|
|
| 3.
|
Enter the amount from Form 1040NR-EZ, line 9
|
3.
|
|
|
|
| 4.
|
Subtract line 3 from line 2
|
4.
|
|
|
|
| 5.
|
Is line 4 more than $50,000?
|
|
|
|
|
| |
![[ ]](graphics/squ.gif) No. No.
|
Skip lines 5 and 6, enter -0- on line 7, and go to line 8.
|
|
|
|
|
| |
![[ ]](graphics/squ.gif) Yes. Yes.
|
Subtract $50,000 from line 4
|
5.
|
|
|
|
| 6.
|
Divide line 5 by $15,000. Enter the result as a decimal (rounded to at least three places). If the result is 1.000 or more, enter 1.000
|
6.
|
|
| 7.
|
Multiply line 1 by line 6
|
7.
|
|
| 8.
|
Student loan interest deduction. Subtract line 7 from line 1. Enter the result here and on Form 1040NR-EZ, line 8
|
8.
|
|
Line 8 - Student Loan Interest Deduction. You may take this deduction only if all three of the following apply.
- You paid interest in 2002 on a qualified student loan (see below).
- Your filing status is single.
- Your modified adjusted gross income (AGI) is less than $65,000. Use lines 2 through 4 of the worksheet below to figure your modified AGI.
Use the worksheet below to figure your student loan interest deduction.
Qualified Student Loan. This is any loan you took out to pay the qualified higher education expenses for yourself, your spouse, or anyone who was your dependent when the loan was taken out. The person for whom the expenses were paid must have been an eligible student (see page 6). However, a loan is not a qualified student loan if (a) any of the proceeds were used for other purposes or (b) the loan was from either a related person or a person who borrowed the proceeds under a qualified employer plan or a contract purchased under such a plan. To find out who is a related person, see Pub. 970.
Qualified higher education expenses generally include tuition, fees, room and board, and related expenses such as books and supplies. The expenses must be for education in a degree, certificate, or similar program at an eligible educational institution. An eligible educational institution includes most colleges, universities, and certain vocational schools. You must reduce the expenses by the following benefits.
- Employer-provided educational assistance benefits that are not included in box 1 of your W-2 form(s).
- Excludable U.S. series EE and I savings bond interest from Form 8815.
- Nontaxable qualified state tuition program earnings.
- Nontaxable earnings from Coverdell education savings accounts.
- Any scholarship, educational assistance allowance, or other payment (but not gifts, inheritances, etc.) excluded from income.
For more details, see Pub. 970.
An eligible student is a person who:
- Was enrolled in a degree, certificate, or other program (including a program of study abroad that was approved for credit by the institution at which the student was enrolled) leading to a recognized educational credential at an eligible educational institution and
- Carried at least half the normal full-time workload for the course of study he or she was pursuing.
Line 9 - Scholarship and Fellowship Grants Excluded. If you received a scholarship or fellowship grant and were a degree candidate, enter amounts used for tuition and course-related expenses (fees, books, supplies, and equipment), but only to the extent the amounts are included on line 5. See the examples in the instructions for line 5 beginning on page 4.
Line 11 - Itemized Deductions. Enter the total state and local income taxes you paid or that were withheld from your salary in 2002. If, during 2002, you received any refunds of, or credits for, income tax paid in earlier years, do not subtract them from the amount you deduct here. Instead, see the instructions for line 4 on page 4.
Note: Residents of India who were students or business apprentices may be able to take the standard deduction instead of their itemized deductions. See Pub. 519 for details.
Line 13 - Exemption Deduction. You can take an exemption of $3,000 for yourself.
Note: Residents of Canada, Mexico, Japan, and the Republic of Korea (South Korea), and U.S. nationals may be able to claim exemptions for their dependents and, if married, their spouse. Residents of India who were students or business apprentices may also be able to take exemptions for their spouse and dependents. However, Form 1040NR must be used to claim the additional exemptions.
Line 16 - Social security and Medicare tax on tip income not reported to employer. If you are subject to social security and Medicare tax, you received tips of $20 or more in any month, and you did not report the full amount to your employer, you must pay the social security and Medicare or railroad retirement (RRTA) tax on the unreported tips. You must also pay this tax if your W-2 form(s) shows allocated tips that you are including in your income on Form 1040NR-EZ, line 3.
To figure the tax, use Form 4137. To pay the RRTA tax, contact your employer. Your employer will figure and collect the tax.
 You may be charged a penalty equal to 50% of the social security and Medicare tax due on tips you received but did not report to your employer.
You may be charged a penalty equal to 50% of the social security and Medicare tax due on tips you received but did not report to your employer.
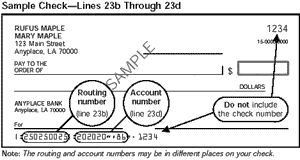
Sample check
Previous| First | Next
Instructions Index | 2002 Tax Help Archives | Tax Help Archives | Home
